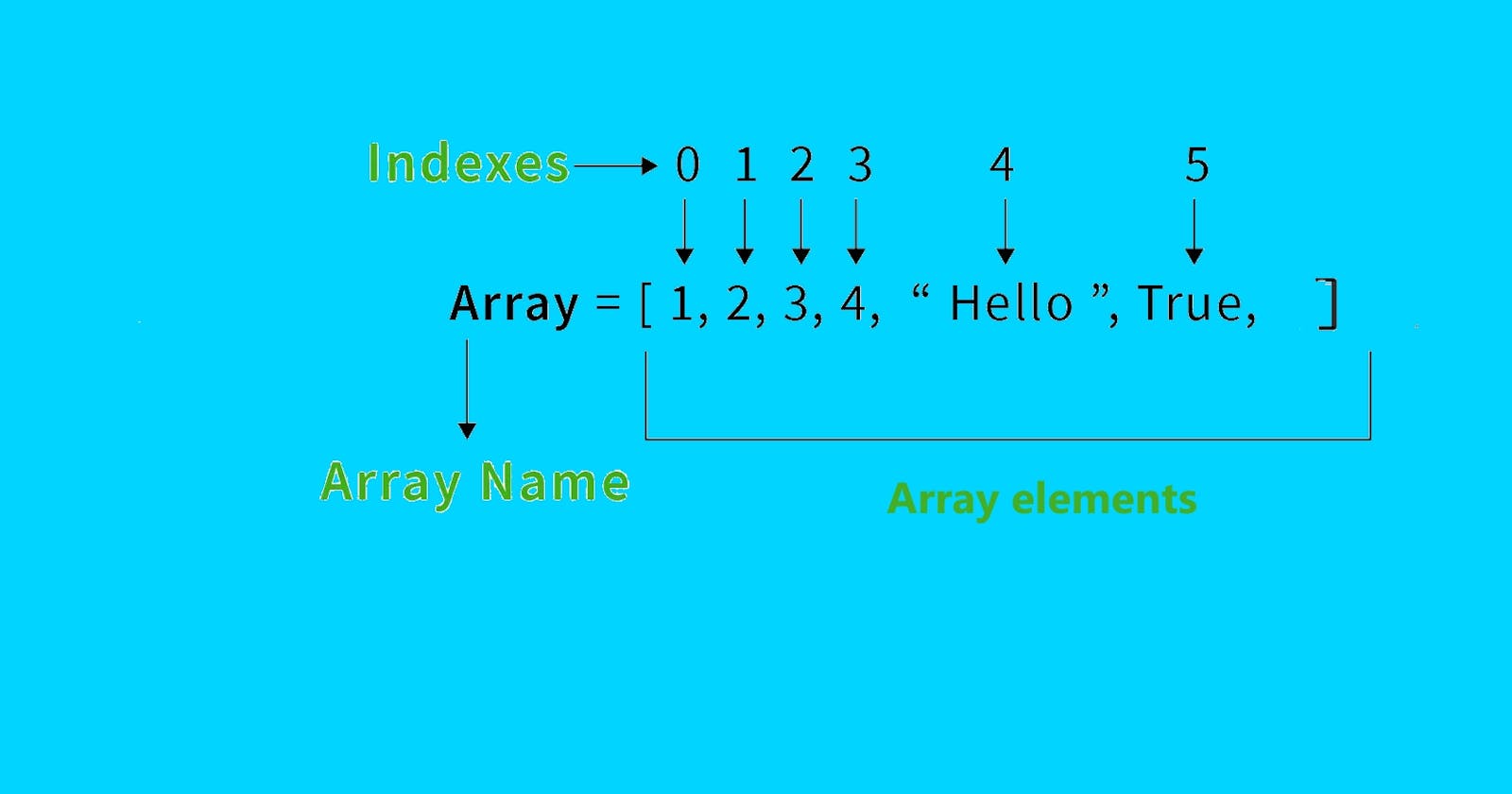
What is an Array?
An array in JavaScript is a fundamental data structure that allows you to store an ordered collection of items under a single variable name. These values can be of any data type, such as numbers, strings, or even other arrays. Arrays are indexed starting from 0 in Js.
typeof array in Js is : object.
Why do we need Arrays in JavaScript?
- Storing large amount of data
- Improving performance
- Ease of use
- Better readability
Grouping related data
Dynamic Size
Creating Arrays:
Generally there are two ways to create a array in Js.
1.Array Literal: Using square brackets [].
// let a = [1, 2, 3, "s", "h", 6.987];
// console.log(a);
// try to find its output by your self
let c =[2,4]
c[10]=33
console.log(c)
2.Array Constructor: This method offers more flexibility but is generally less used.
//let a = new Array()
//console.log(a) //print a null array
// let b = new Array("hii",23,4.4,"gopal")
// console.log(b)
// let c= new Array(4.4)
// console.log(c) // this will give error
//let d = new Array(3)
//console.log(d) // // Creates an array with 3 empty slots
Accessing Elements of array:
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
console.log(a);
// // to find length of array
console.log( a.length)
//console.log( a.length()) // be cautious this will give an error
console.log(a[3]) //this will print j which is 4th element as
//index start from 0
// // to access all elements
for(let i =0 ;i<a.length;i++)
{
console.log(a[i])
}
//note : try to access the element outside the size of array
Common Array Methods:
push(): Adds one or more elements to the end of the array.
pop(): Removes and returns the last element from the array.
update(): we can update at any position in an array in js.
shift(): Removes and returns the first element from the array.
unshift(): Adds one or more elements to the beginning of the array.
slice(): Extracts a section of the array and returns a new array.
concat(): Merges two or more arrays and returns a new array.
join(): Joins all elements of an array into a string, separated by a specified separator.
reverse(): To reverse the array.
indexof(): to find index of any element of an array.
splice(): Used to add new items at given position:
it has its syntax: array.splice(start, deleteCount, item1, item2, ...)find(): method is used to search for an element in an array that satisfies a specified condition.
Try to run following codes by yourself for better understanding.
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
a.push(10,12);
console.log("array after pushing",a);
// //pop
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
a.pop()
console.log("array after deletion",a)
// //update;
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
a[2]= "updated"
console.log(a)
// //shift
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
let r= a.shift()
console.log("array after DELETING first",r,a);
console.log("array after DELETING first : ",a);
// //unshift
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
a.unshift('10')
console.log("array after pushing ",a);
// //slice
let a =[0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
// console.log(a.slice(2)) // print all from index two to till last
console.log(a.slice(1,4)) // print from index 1 to n-1 i.e 3 int this case
// //concat
let a =[1,2,3,4]
let b= [4,5,6,6]
let c=[6,7,8,9]
let d = a.concat(b,c)
console.log(d)
// // join
let a =[1,2,3,4]
let e = a.join("+")
console.log(e)
// // for reverse
let r = [1,2,3,45,"hi"]
console.log(r.reverse())
//r =r.reverse() // or
//r.reverse
//console.log(r)
// // to find index
let a = [1, 2, 3,'j', "g", "s", 6.987];
console.log(a.indexOf(3))
console.log(a.indexOf(7)) // return -1
// // splice
let fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date"];
// //Remove 1 element starting from index 2
let removed = fruits.splice(2, 1);
// fruits is now ["apple", "banana", "date"], and removed is ["cherry"]
// Remove 2 elements starting from index 1, and replace them with "kiwi" and "lemon"
fruits.splice(1, 2, "kiwi", "lemon");
// fruits is now ["apple", "kiwi", "lemon", "date"]
// // // splice
let m = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6]
// m.splice(1,0,11)
// m.splice(-14,0,111)
// console.log(m)
// m.splice(-2,0,11)
// console.log(m)
// m.splice(2,2,11)
// console.log(m)
m.splice(16,0,77)
console.log(m)
// // find
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let found = numbers.find(function(element) {
return element > 2;
});
console.log(found);
lt.32link: https://hashnode.com/post/cltkjjbk300000ala2hkm89un